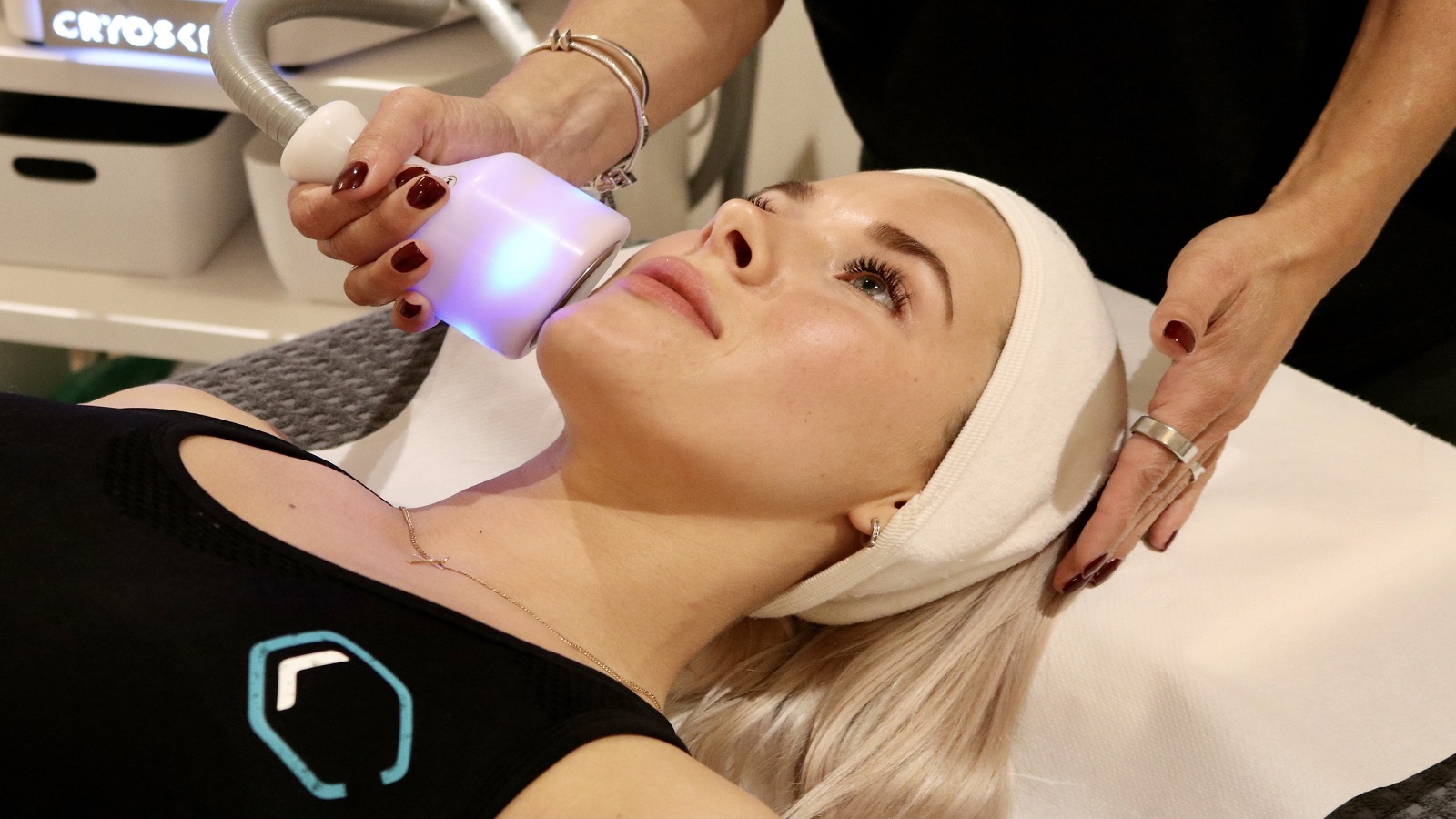
Cryotherapy is a treatment that uses extreme cold to freeze and remove abnormal tissue. It is commonly used for various medical conditions, including skin disorders, cancer treatment, and muscle recovery. Here’s a detailed overview of cryotherapy:
Types of Cryotherapy:
- Local Cryotherapy:
- Cryosurgery: Used to treat localized areas, such as skin lesions, warts, and certain types of tumors. Liquid nitrogen is commonly used.
- Cryofacial: A beauty treatment that applies cold air to the face to rejuvenate the skin.
- Whole-Body Cryotherapy (WBC):
- Procedure: The individual stands in a cryotherapy chamber or tank that surrounds the body, excluding the head, with temperatures ranging from -100°C to -140°C (-148°F to -220°F) for 2-4 minutes.
- Applications: Commonly used by athletes for muscle recovery, reducing inflammation, and enhancing overall wellness.
Uses of Cryotherapy:
- Medical Treatments:
- Dermatology: Treats skin conditions such as warts, moles, skin tags, and actinic keratosis.
- Oncology: Used to treat certain cancers, including prostate, liver, and cervical cancer, by freezing cancerous cells.
- Pain Relief and Muscle Healing: Reduces inflammation and pain in muscles and joints.
- Cosmetic Treatments:
- Skin Rejuvenation: Enhances skin tone, reduces wrinkles, and tightens skin.
- Weight Loss: Claims to boost metabolism and aid in weight loss (though scientific evidence is limited).
- Sports and Fitness:
- Recovery: Accelerates muscle recovery and reduces soreness after intense physical activity.
- Performance Enhancement: Claims to improve athletic performance by reducing muscle fatigue and inflammation.
Procedure of Cryotherapy:
- Preparation:
- For local cryotherapy, the area to be treated is cleaned and prepared.
- For whole-body cryotherapy, individuals wear minimal clothing (typically underwear), along with gloves, socks, and protective ear and mouth coverings.
- Treatment:
- Local Cryotherapy: Liquid nitrogen is applied directly to the targeted area using a spray device or cotton swab.
- Whole-Body Cryotherapy: The individual enters the cryotherapy chamber and remains there for the duration of the treatment.
- Post-Treatment Care:
- Localized treatments may result in redness, blistering, or scabbing, which typically heal over time.
- For whole-body cryotherapy, normal activities can usually be resumed immediately after the session.
Benefits of Cryotherapy:
- Reduced Inflammation: Helps decrease inflammation in joints and muscles.
- Pain Relief: Alleviates chronic pain and muscle soreness.
- Improved Recovery: Speeds up recovery time for athletes.
- Enhanced Skin Health: Improves skin appearance and reduces signs of aging.
Risks and Considerations:
- Skin Damage: Risk of frostbite, burns, or scarring if not done correctly.
- Temporary Side Effects: Numbness, tingling, redness, or irritation in the treated area.
- Not Suitable for Everyone: People with certain medical conditions (such as cold allergies, cardiovascular issues, or nerve damage) should avoid cryotherapy.
- Limited Scientific Evidence: Some claimed benefits, particularly for whole-body cryotherapy, lack robust scientific support.
Choosing a Provider:
- Licensed Professional: Ensure treatments are administered by trained and certified professionals.
- Reputable Facility: Choose a clinic with a good reputation and adherence to safety standards.
- Consultation: Have a thorough consultation to determine if cryotherapy is suitable for your condition or goals.
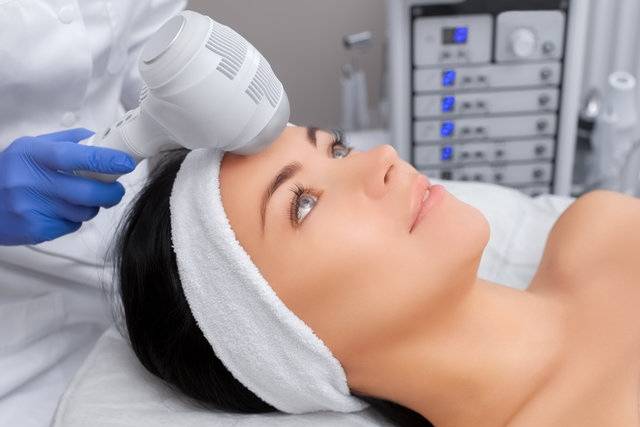
Cryotherapy can offer significant benefits for certain medical and cosmetic conditions, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if it’s appropriate for you and to ensure it’s performed safely.