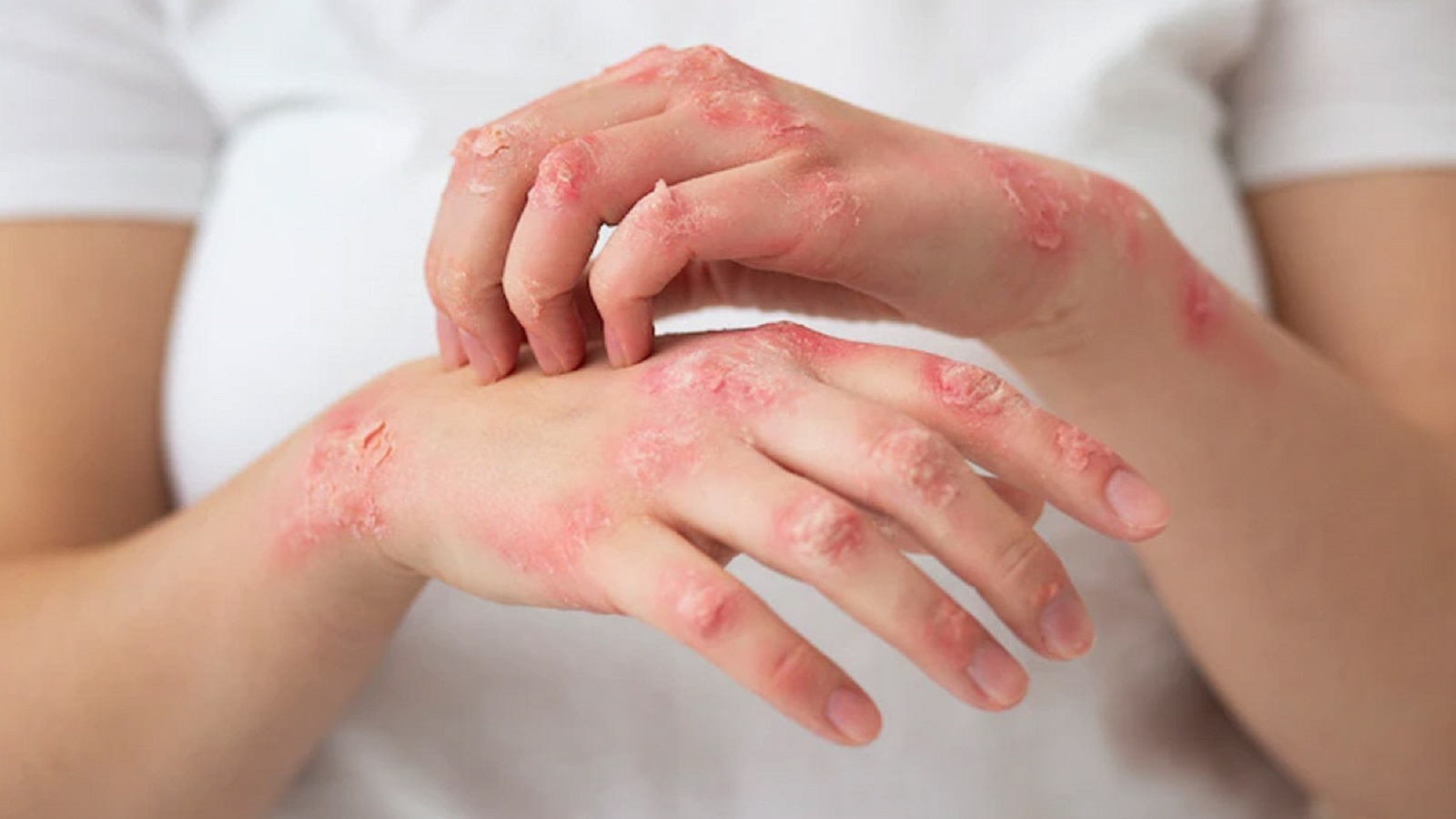
Itching, urticaria, fungal infections, psoriasis, eczema, and pigmentary disorders are common skin conditions that can affect individuals in various ways. Here’s an overview of each:
Itching (Pruritus):
- Causes:
- Dry skin
- Allergies
- Insect bites
- Skin conditions (eczema, psoriasis)
- Systemic conditions (liver disease, kidney failure)
- Management:
- Moisturizers: To hydrate the skin.
- Antihistamines: For allergy-related itching.
- Topical Steroids: To reduce inflammation.
- Cool Compresses: To soothe irritated skin.
Urticaria (Hives):
- Symptoms:
- Red, raised, itchy welts on the skin.
- Can appear anywhere on the body.
- Often triggered by allergens, stress, infections, or medications.
- Management:
- Antihistamines: To relieve itching and reduce hives.
- Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding known triggers.
- Cool Compresses: To reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Corticosteroids: For severe cases.
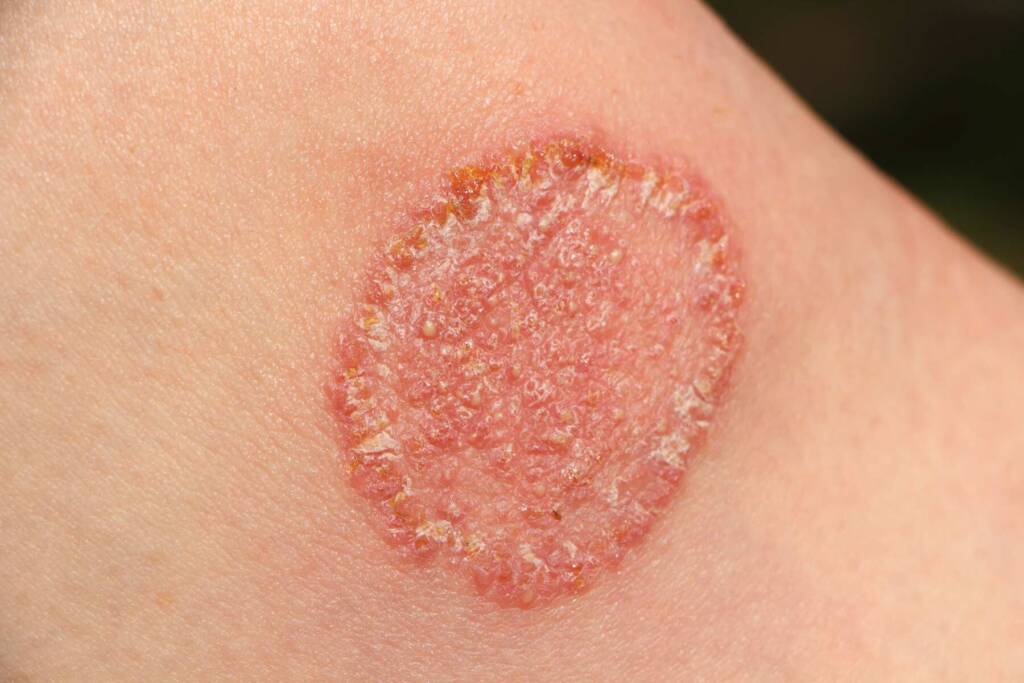
Fungal Infections:
- Types:
- Tinea (Ringworm): Affects skin, scalp, feet (athlete’s foot), and nails.
- Candida: Affects mucous membranes, such as in oral thrush or vaginal yeast infections.
- Symptoms:
- Itchy, red, scaly patches.
- Ring-shaped rashes (for tinea).
- White patches in the mouth or on the tongue (for candida).
- Management:
- Antifungal Creams or Ointments: For topical infections.
- Oral Antifungal Medications: For more severe or systemic infections.
- Good Hygiene: Keeping the affected area clean and dry.
Psoriasis:
- Symptoms:
- Red, scaly patches of skin.
- Often on elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
- Itching and pain.
- Management:
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and moisturizers.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet light under medical supervision.
- Systemic Medications: Oral or injected medications to reduce immune system activity.
- Biologics: Target specific parts of the immune system.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis):
- Symptoms:
- Itchy, red, and inflamed skin.
- Common in children, but can occur at any age.
- Often affects the face, hands, and inside of elbows and knees.
- Management:
- Moisturizers: Regular use to prevent dryness.
- Topical Steroids: To reduce inflammation.
- Antihistamines: To relieve itching.
- Avoid Triggers: Such as certain soaps, fabrics, or foods.
Pigmentary Disorders:
- Types:
- Vitiligo: Loss of skin color in patches.
- Melasma: Dark, discolored patches on the skin.
- Hyperpigmentation: Darkening of an area of skin caused by increased melanin.
- Management:
- Topical Treatments: Hydroquinone, corticosteroids, and retinoids for hyperpigmentation.
- Phototherapy: UV light therapy for vitiligo.
- Cosmetic Procedures: Chemical peels, laser therapy, or microdermabrasion for melasma and hyperpigmentation.
- Sun Protection: Using sunscreen to prevent further pigmentation changes.
General Tips for Skin Care:
- Hydration: Keeping the skin moisturized to prevent dryness and itching.
- Avoid Irritants: Such as harsh soaps, fragrances, and allergens.
- Healthy Diet: Nutrient-rich diet to support skin health.
- Stress Management: As stress can exacerbate many skin conditions.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: For ongoing management and monitoring of chronic skin conditions.
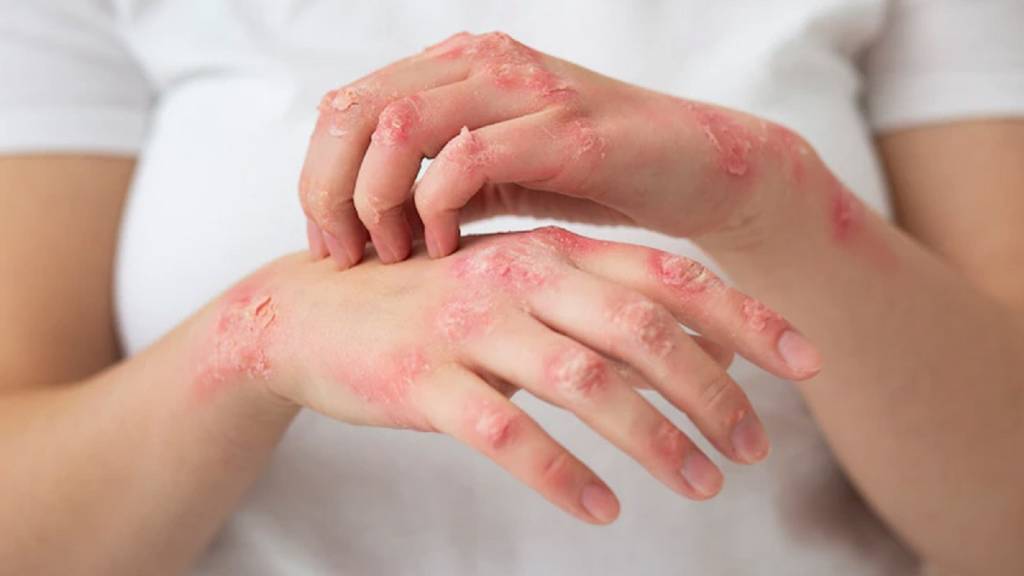
Consulting with a dermatologist is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans for any skin condition.