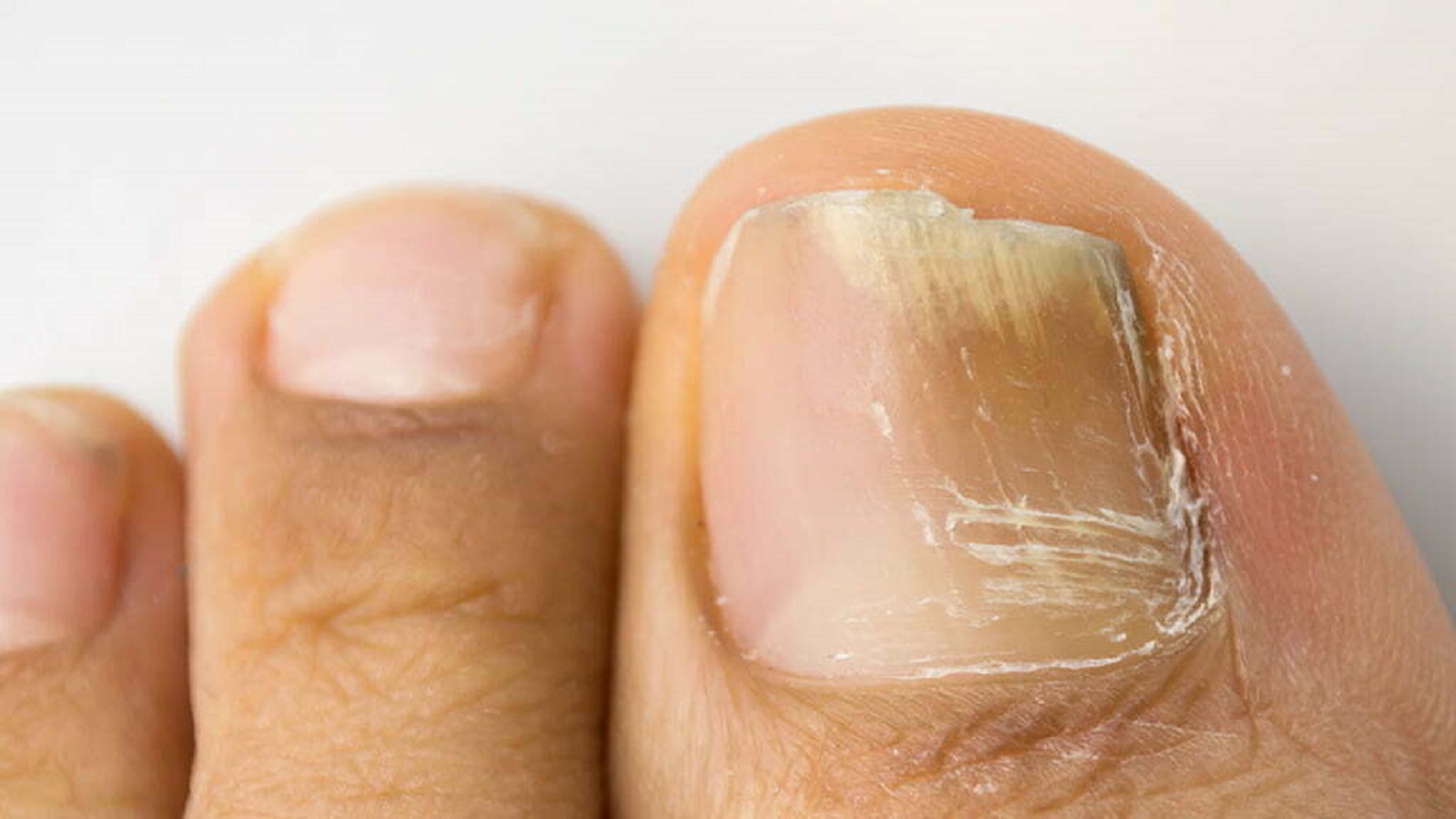
A nail fungal infection, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects the nails, typically the toenails more often than fingernails. It’s caused by fungi such as dermatophytes, yeasts, or molds. Here’s a detailed overview of nail fungal infections:
Causes:
- Fungi: Dermatophytes (most common), yeasts (Candida species), or molds.
- Risk Factors:
- Warm and Moist Environments: Such as sweaty shoes and socks.
- Trauma: Injuries to the nail or surrounding skin.
- Poor Nail Hygiene: Not keeping nails clean and trimmed.
- Reduced Immunity: Conditions like diabetes or immune system disorders.
Symptoms:
- Thickened Nails: Nails may become thicker and more brittle.
- Discoloration: Yellowish or white spots or streaks on the nail.
- Distorted Shape: Nails may change shape or become crumbly.
- Brittleness: Nails can break easily.
- Pain or Discomfort: Especially if the infection progresses.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical Examination: Visual inspection of the nails.
- Microscopic Examination: Nail clippings or scrapings are examined under a microscope to identify the fungus.
- Culture: Fungal cultures may be done in cases where the diagnosis is uncertain.
Treatment Options:
- Topical Antifungal Medications:
- Creams or Ointments: Applied directly to the affected nail and surrounding skin.
- Nail Lacquers: Special nail polish-like applications that are applied to the nail.
- Oral Antifungal Medications:
- Prescription Medications: Taken orally for a specified period (typically several weeks to months).
- Monitor Liver Function: Some oral antifungals require monitoring liver function due to potential side effects.
- Surgical and Other Procedures:
- Nail Removal: In severe cases or when other treatments haven’t been effective.
- Laser Therapy: Emerging as a treatment option to target the fungus.
- Home Remedies and Care:
- Good Nail Hygiene: Keep nails clean, dry, and trimmed.
- Avoid Nail Trauma: Protect nails from injury.
- Antifungal Powders or Sprays: Applied to shoes and socks to prevent re-infection.
Prevention:
- Proper Foot and Nail Hygiene: Keep nails clean, dry, and trimmed.
- Avoid Barefoot Walking: Especially in public showers or swimming pools.
- Change Socks Regularly: Especially if they become sweaty.
- Avoid Tight Footwear: Wear shoes that allow air circulation.
- Use Antifungal Products: Especially if prone to fungal infections.
Complications:
- Spread of Infection: To other nails or skin.
- Chronic Infection: If not treated promptly or effectively.
- Secondary Bacterial Infection: Due to breaks in the skin.
When to See a Doctor:
- Persistent Symptoms: If over-the-counter treatments aren’t effective.
- Pain or Discomfort: Especially if accompanied by other symptoms.
- Diabetes or Other Health Conditions: Increased risk of complications.
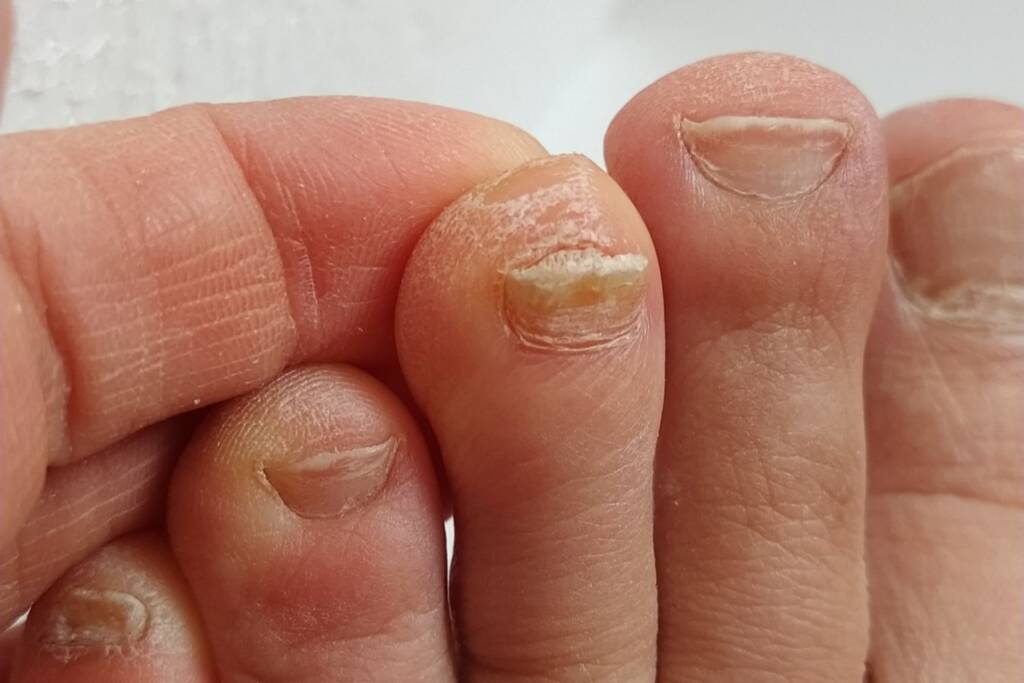
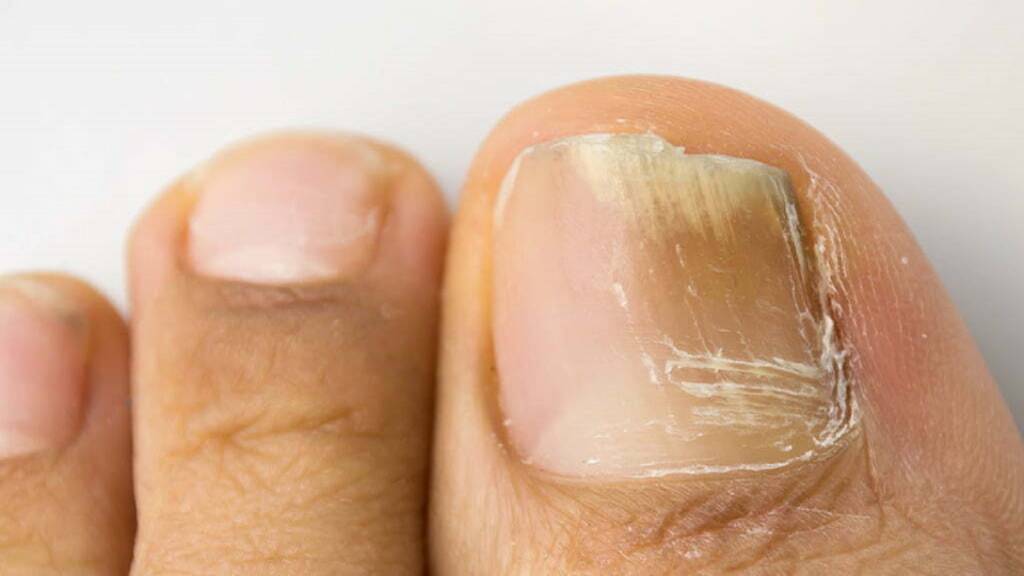
Nail fungal infections can be persistent and challenging to treat, requiring consistent and appropriate treatment measures. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the best treatment plan based on the severity and type of infection.